
Contact Info
2055 Limestone Road, STE 200-C in Wilmington, DE 19808
(888) 702-7866
info@rshosting.com
Live ChatRecommended Services
Supported Scripts
What Is Redundant Array of Independent Disks (RAID) Storage?
What Is Redundant Array of Independent Disks (RAID) Storage?
RAID storage:- combines multiple storage drives into a single logical unit. Think of it as teamwork for your storage drives.They work together to either speed up your system, protect your data, or both.
When you set up RAID, your computer treats multiple physical drives as one drive. This setup can dramatically improve performance, provide data backup protection, or deliver both benefits depending on which RAID level you choose.
Understanding RAID levels (RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 5, RAID 6, RAID 10) and how they work:-
A RAID controller is the hardware or software that manages a RAID setup. Different RAID “levels” exist, and each one is designed for specific needs like speed, data protection, or both.
Before choosing a RAID level, decide what matters most to you—performance, data safety, or cost.
- For basic speed or simple data protection, lower RAID levels with a few normal hard drives are enough.
- For high performance and strong data protection, you need special RAID-ready hard drives and more disks.
Each RAID level has its own setup, benefits, and requirements. The most common RAID levels are described below.
RAID 0: Maximum Performance
RAID 0 splits your data across two or more drives so they can work at the same time.
This gives very fast read/write speeds. But if any one drive fails, all data is lost.
Benefits:
- Very fast data transfer
- Uses full storage capacity
- Good for high-performance tasks
Considerations:
- No data protection—one drive failure means total data loss
- Performance can vary with certain workloads
Example: RAID 0 with 3 drives splits data across all three for maximum speed.

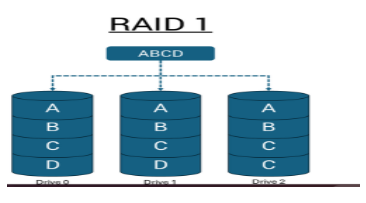
RAID 1 (mirroring)
RAID 1 (mirroring) creates an identical copy of everything on two drives. Every file you save gets written to both drives simultaneously, creating a perfect mirror. All I/O operations must be performed identically to both drives, thus variations in drive performance when the models are different result in the I/O operations completing only as fast as the slowest drive.
Benefits:
- Complete data redundancy—if one drive fails, your data remains safe
- System continues running normally with just one working drive
- Perfect for important documents, business data, and irreplaceable files
Considerations:
- Uses only half of your total drive capacity for storage
- Performance limited by the slower drive in mismatched pairs
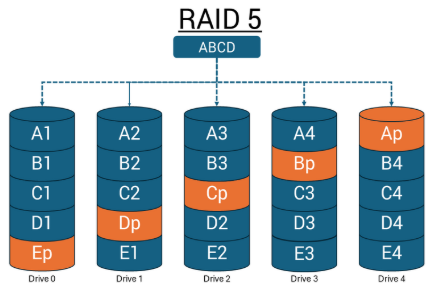
RAID 5: Striping with Parity
RAID 5 spreads data and parity (error-checking info) across at least three drives. If one drive fails, the system can rebuild the missing data using the parity.
Performance:
- Faster reads (data comes from multiple drives)
- Slower writes (parity must be calculated and written)
Redundancy:
- Can survive one drive failure and rebuild the data
Storage Efficiency:
- Storage equal to one entire drive is used for parity
Use Case:
Often used in servers for a good balance of speed, storage efficiency, and data protection.
RAID 6 (striping with double parity):
RAID 6 works the same way as RAID 5, but with double parity: parity data is duplicated and spread across disks in a RAID 6 in a way that it can suffer up to two simultaneous disk failures, and still be able to fully rebuild all data that was stored. RAID 6 requires at least 4 disks.
Performance:
Faster read performance due to multiple simultaneous reads, but slower write performance due to multiple parity calculations.
Redundancy:
High, two concurrent disk failures can occur with no data loss.
Storage Efficiency:
Two disks worth of storage space are lost to parity data.
RAID 6 is popular in situations where RAID 5 does not guarantee enough fault tolerance.

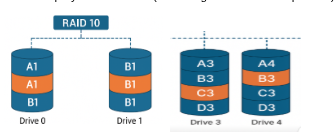
RAID 10 (combined mirroring and striping)
RAID 10 (1 + 0) is a nested RAID configuration consisting of RAID 1 and RAID 0 in combination. RAID 10 takes mirrored RAID 1 arrays and then stripes them in RAID 0, resulting in high speed as well as high redundancy. You can also have RAID 01 (with the mirroring and striping reversed from RAID 10), however as it offers less fault tolerance with the same storage requirements, it is not recommended.
Performance;
High read and write performance, comparable to a RAID 0 configuration.
Redundancy:
High, due to mirroring. More than two mirrors can be present for higher redundancy.
Storage Efficiency:
At least four disks are required for RAID 10, and only 50% of the total storage space is available as the rest is taken up by mirrored data (assuming two mirrors are present).
Some RAID levels can be combined, such as RAID 50, which uses RAID 5 arrays striped together with RAID 0. This gives higher speed and better protection but needs at least 6 drives.
RAID setups are not standardized, so different hardware or software may use slightly different methods. Always check what your system supports.
There are also older RAID types like RAID 2, 3, and 4, but they are rarely used because they do not offer real advantages over the common RAID levels.
Types of RAID Controller:
Hardware-based RAID
Uses a dedicated physical controller to manage hard drive.
- Offers high speed and reliability
- Can work independently from the system’s processor
- Often built into the motherboard or as a separate card
Software-based RAID
Uses the system’s processor and memory to manage RAID.
- No special hardware required
- Cost-effective, but may reduce overall system performance
- Slower than hardware RAID
Network attached storage (NAS):
Many consumer and professional NAS devices offer RAID out of the box — just add your own drives, set the RAID level, and you’re set.
Managing Resiliency and Integrity in RAID for Mission-Critical Data
RAID is not a complete solution for preventing data loss. Even a large RAID array can fail due to misconfiguration, theft, fire, or natural disasters.
A common problem is that a disk fails and no one notices. This is why it’s important to monitor your RAID system using a reliable remote monitoring and management tool. You should also keep backups or off-site copies of your data for disaster recovery.
